Pain Management
Pain management can be simple or complex, depending on the origin of the pain. An example of less complex pain is nerve root irritation from a herniated disc with pain spreading down the leg. This ailment is frequently relieved by an epidural steroid injection and physiotherapy. However, the occurrence of pain increases with age and all pains are not treatable. Therefore, pain control is an important part of your care.
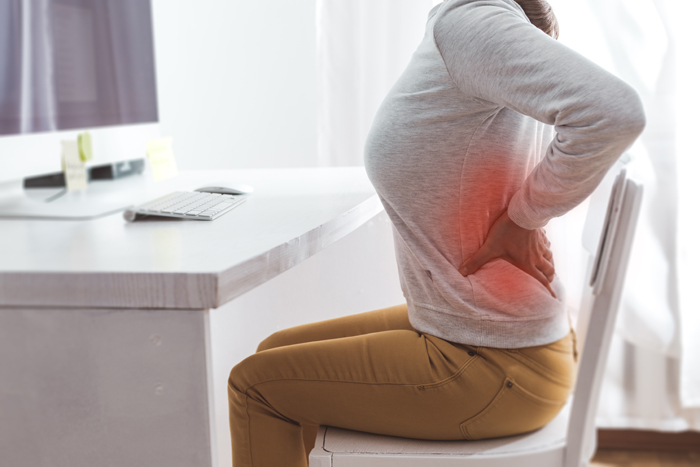

What Are the Types of Pains?
There are several forms and causes of pain, which may be classified into eight categories:
- Acute pain: Natural response to an accident or a medical condition. It generally begins abruptly and lasts only a few minutes. Chronic pain: Discomfort that lasts longer than intended. It usually lasts longer than 3 months.
- Breakthrough pain: Sudden, brief, and intense pain in persons who are already using drugs to treat chronic pain.
- Bone pain: Pain, aching, or soreness in one or more bones that occurs during both exercise and rest.
- Nerve pain: Caused by nerve injury or inflammation. The pain is typically characterized as acute, shooting, searing, or stabbing.
- Phantom pain: Pain that appears to come from a bodily part that no longer exists. It is prevalent in people who have had a limb amputated, but it is not the same as phantom limb feeling, which is typically painless.
- Soft tissue pain: Caused by muscle, tissue, or ligament injury or inflammation. It is often coupled with swelling or bruising.
- Referred pain: Pain that appears to be emanating from one site but is caused by an injury or inflammation in another tissue or organ. During a heart attack, for example, pain is frequently felt in the neck, and down the right arm.
What are the symptoms of pain?
Sometimes the pain is just one of many symptoms, which include:
- A dull ache
- Not feeling well
- Burning
- Trouble sleeping
- Squeezing
- Stinging
- Soreness
- Stiffness
- Weakness
What Are the Causes of Pain?
The most common causes of pain in adults include:
- Injury
- Medical conditions (such as cancer, arthritis, and back problems)
- Surgery
- Compression fractures
- Plantar fasciitis
- Cancer pain
When to See a Doctor?
Over-the-counter pain medicine helps subside the acute pain for a few hours, but pain could always reverse. It is better to discuss any medicines with your pain management doctor before taking them and identify the origin of pain and the ways to minimize it. Older people have an increased risk of side effects on drugs.
Request an appointment at Apollo Spectra Hospitals
Call 18605002244 to book an appointment
What is the Treatment of Pain Management?
There are several non-medical remedies available to help you manage your pain. A mix of treatments and therapies is frequently more beneficial than a single treatment or therapy.
- Hot and cold packs: To minimize swelling, apply ice packs immediately after an accident. Heat packs are more effective for treating chronic muscle or joint ailments.
- Physical therapy: Walking, stretching, strengthening, and aerobic activities can help alleviate discomfort, keep you flexible, and enhance your mood.
- Acupuncture: It includes the insertion of tiny needles into particular spots on the skin. It seeks to rebalance the body and facilitate healing by releasing natural pain-relieving compounds (endorphins).
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy: Electrical currents of varying voltages travel through the skin through electrodes, eliciting a pain-relieving reaction from the body. Some persons with chronic pain who are resistant to conventional therapies may benefit from it.
Pain medications
- Paracetamol: Prescribed as the first drug to alleviate acute pain.
- Aspirin: Used to treat fever and mild-to-moderate pain in the short term (such as period pain or headache).
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, alleviate pain and decrease inflammation (redness and swelling).
- Opioid medications, such as codeine, morphine, and oxycodone, are designated for severe or cancer pain.
- Local anesthetics (drops, sprays, creams, or injections) are used when nerves are easily available.
Conclusion
Pain management helps speed recovery and minimizes the likelihood of complications such as pneumonia and blood clots. This means your pain control allows you to take deep breaths and cough, get out of bed, walk in the hallway, do the exercises and therapy important to your recovery and, in general, improve your overall quality of life.
Work with your general surgeon or search pain management hospitals near me, to create the best plan of care suitable for your needs.
When patients are taking painkillers for a long time, they can become addicted. To minimize the risk of addiction to painkillers, you should only take the drugs as prescribed. If your doctor has given you the drug as needed, do not take it. Only take it when you have the pain and discuss the use and concerns with your doctors.
A common misconception in pain management is that weight does not affect your pain. Weight actually contributes to a lot more pain. Severe obesity in the elderly increases the risk of chronic pain. There have been studies that show that a decrease in 10% of your weight can drastically reduce your pain.
Realistic goals for pain control are to keep pain at a lower level and from becoming severe. Controlled pain does not mean that you will be pain free, some amount of discomfort can be expected and is normal. As you recover, you become more active. Well-controlled pain means you are able to do the activities you need to do to recover without experiencing severe pain.
Our Doctors
DR. SHRIRAM GAUTAM
MD (Anaesthesiology)...
| Experience | : | 1 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Critical Care/Pain M... | Location | : | Ratahara |
| Timings | : | Mon - Sat : 10:00 AM... |
DR. SHRUTI BACHALLI
MBBS, MD (Anaesthesi...
| Experience | : | 16 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | Koramangala |
| Timings | : | Available by prior a... |
DR. KARTHIC BABU NATARAJAN
MBBS,MD, DNB...
| Experience | : | 13 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | MRC Nagar |
| Timings | : | On Call... |
DR. SHEERIN SARAH LYSANDER
MBBS, MD(Anesthesiol...
| Experience | : | 8 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | MRC Nagar |
| Timings | : | Mon - Sun : 7:00 AM ... |
DR. SORABH GARG
MBBS, DNB (Anaesthes...
| Experience | : | 16 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | Karol Bagh |
| Timings | : | Mon - Sat : 9:00 AM ... |
DR. TUSHAR B MUNNOLI
MBBS, MD - Anaesthes...
| Experience | : | 8 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | Koramangala |
| Timings | : | Wed : 11:00 AM to 2:... |
DR. SURBHI P. BHAGAT
MBBS, MD - Anaesthes...
| Experience | : | 21 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | Tardeo |
| Timings | : | Mon to Sat : 01:00 P... |
DR. UTTAM ANANT SIDHAYE
MBBS, MD, FIAPM...
| Experience | : | 21 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | Sadashiv Peth |
| Timings | : | Mon to Sat : 1:00 PM... |
DR. AVNEET SAINI
MBBS, MD, FIAPM...
| Experience | : | 4 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | Tardeo |
| Timings | : | Mon to Sat : 1:00 PM... |
DR. SUKHDEO SATYANARAYAN GUPTA
MBBS, DA, DNB (Anaes...
| Experience | : | 6 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | Tardeo |
| Timings | : | Mon to Sat : 1:00 PM... |
DR. MURALIDHAR T S
MBBS, MD (Anaesthesi...
| Experience | : | 25 Years Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Speciality | : | Pain Management... | Location | : | Koramangala |
| Timings | : | Sun : 9:00 AM to 5:0... |
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment












.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








