5 Best Ways to Treat Knee Pain
November 24, 2025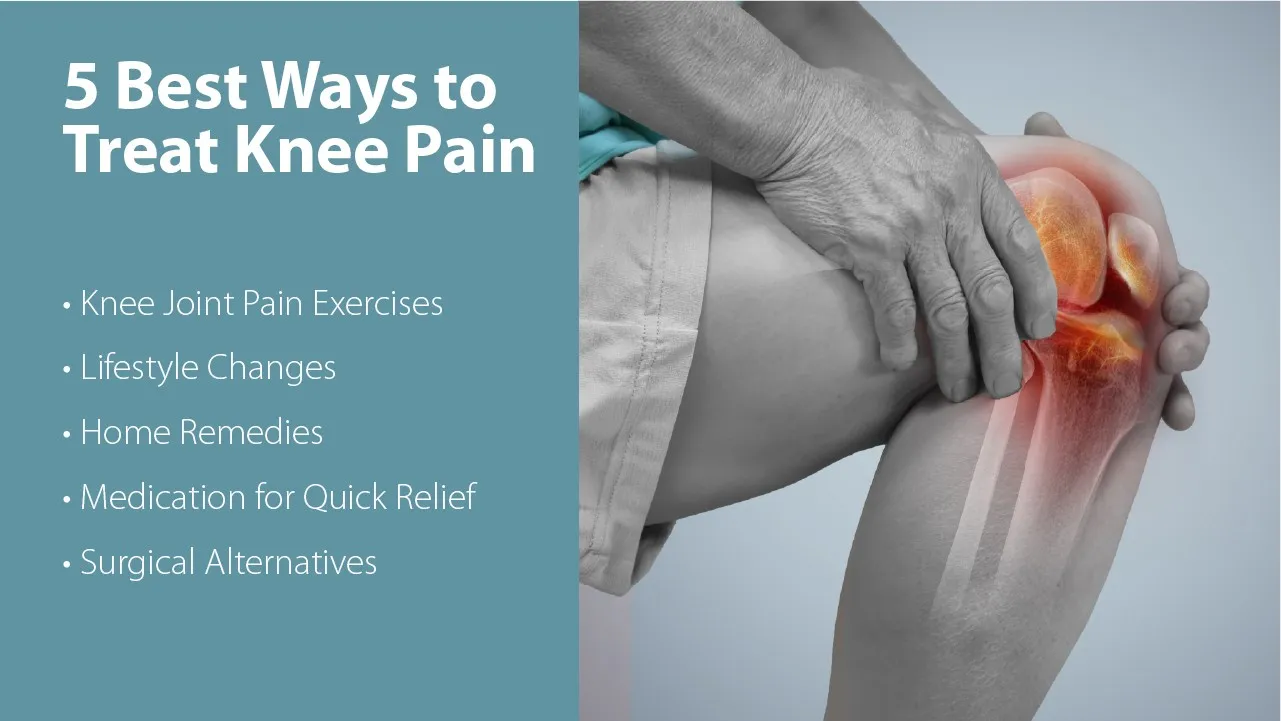
Knee pain is one of the most prevalent joint complaints worldwide. According to the Arthritis Foundation, over 60 million people experience arthritis (a type of knee pain) that limits their ability to perform daily activities freely. This can be brought on by trauma, excessive use, obesity, or diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
As the knee supports a major portion of the body weight, even small problems can affect your mobility, comfort and quality of life. You don't need to worry. The majority of knee pain can be effectively managed without surgery and with treatment options such as prescription drugs, physical therapy, a healthy diet, daily habit modifications and more. So, if you are wondering how to relieve knee pain naturally, keep reading to learn the 5 best treatments for chronic knee pain.
Top 5 Methods for Knee Pain Relief
People of all ages can experience knee pain. It can occur suddenly or gradually as a result of age-related wear and tear, injuries, or excessive use. Whether you have arthritis, a strained muscle, an injury, or inflammation will determine the best course of action. Often, a mix of methods is most effective. Here are five expert-recommended, evidence-based strategies for effectively managing and relieving knee pain:
- Medication for Quick Relief
The first line of treatment for knee pain is medication, particularly if the symptoms develop suddenly or become severe.
OTC (Over-The-Counter) Drugs
NSAIDs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, include naproxen sodium (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil). They function by lessening joint pain and inflammation. Although it doesn't lessen inflammation, acetaminophen (Tylenol) can be used for people who can't take NSAIDs.
Dosage Recommendations
Adults should take 400–1,200 mg of ibuprofen per day, though this depends on their age, body weight, and kidney function. Before beginning or modifying any medication, always get your doctor's approval.
Topical Pain Relievers
Diclofenac or capsaicin-containing creams or gels can be applied topically to the skin above the knee. For localised osteoarthritis pain, these are particularly helpful. These choices are perfect for managing flare-ups or for short-term use. However, they are best used along with long-term strategies because they do not address the root cause.
- Home Remedies for Knee Pain
When it comes to mild to moderate cases of knee pain, a number of natural remedies have proven to be effective. The most common knee pain home remedies are discussed as follows:
Heat and Ice Therapy
To lessen swelling and dull acute pain, apply ice packs. You can apply them multiple times throughout the day for 15 to 20 minutes. To relieve stiffness, use heat therapy with a heated pad or towel to increase blood flow and ease tense muscles.
Turmeric And Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Turmeric contains curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory. It can be taken as a supplement or added to food. However, you should first consult with your doctor if you are dealing with an underlying issue. You can also incorporate foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, to help naturally reduce joint inflammation.
Rest, Elevation and Compression
If you are asking what helps knee pain fast, focus on the basics: rest, ice, compression, and elevation, commonly known as the RICE method. Therefore, you must stay away from strenuous exercise. To help drain extra fluid and lessen swelling, you can also elevate your leg with pillows. Moreover, you can also apply an elastic compression bandage to your knee. It promotes healing and stabilises the joint. Just make sure you don't wrap it too tightly.
These natural treatments for knee pain work particularly well for early-stage discomfort and can frequently stop the pain from getting worse.
Also Read: Robotic knee replacement surgery
- Lifestyle Changes for Prolonged Relief
Changing habits that may be causing your pain is important for long-term management. These are among the best treatments for chronic knee pain when surgery is not yet required.
Weight Control
Having excess weight puts more strain on your knees. In actuality, your knees experience an extra 4 kg of pressure for every kilogram of excess weight. Chronic knee pain can be considerably reduced by losing even a small amount of weight, especially for those who have osteoarthritis.
Awareness Of Posture
Bad posture when standing or sitting can put more strain on the knee joint. Avoid standing with your knees locked or sitting cross-legged for extended periods of time to maintain proper posture. Make use of chairs that provide adequate knee and back support.
Diet And Supplements
Make sure your diet contains foods high in calcium, vitamin D, and leafy greens. Your doctor might recommend supplements to enhance joint health if you are lacking in omega-3 fatty acids or vitamin D.
Assistive Devices
When advised, wear orthotic shoe inserts, walking aids, or knee braces. These can lessen walking pain, enhance balance, and support your knees. For those who experience chronic or recurrent pain, these minor adjustments, when made regularly, provide long-lasting advantages.
- Knee Joint Pain Exercises
While inactivity frequently exacerbates knee pain, many people are concerned that exercise may exacerbate it. Stiffness is decreased, flexibility is increased, and the muscles surrounding the knee are strengthened with controlled movement. Try these safe and efficient exercises for knee joint pain:
|
Exercise |
Target Muscles |
Purpose |
Precautions |
|
Quadriceps Stretch |
Quadriceps (front thigh) |
Improve flexibility and support the knee cap |
Hold the ankle gently; avoid jerking movements |
|
Hamstring Curls |
Hamstrings (back of thigh) |
Strengthen rear thigh muscles |
Do not overextend; start with low repetitions |
|
Leg Raises |
Quadriceps, Hip Flexors |
Build strength around the knee joint |
Keep movements slow and controlled |
|
Water Aerobics / Swimming |
Full lower body |
Provide resistance with joint protection |
Use shallow water if balance is an issue |
|
Walking |
Quadriceps, Hamstrings, Calves |
Improve circulation and mobility |
Avoid uneven surfaces; use supportive shoes |
|
Cycling (Stationary) |
Thigh and calf muscles |
Low-impact cardio that strengthens the knee |
Adjust seat height to avoid strain on the knee joint |
Before working out, always warm up, and if you experience sudden pain, stop. For a customised plan, speak with a physiotherapist.
- Surgical Alternatives for Complex Situations
Surgery may be required if conservative measures are ineffective or if the damage is huge. Usually, this is saved for cases of severe arthritis, trauma, or instability. The primary surgical options are as follows:
Total Knee Replacement
A complete or total knee replacement involves the replacement of the entire knee joint with artificial parts, typically composed of medical-grade plastic and metal. Patients with severe osteoarthritis, where the cartilage has entirely worn away and is causing persistent pain, swelling, and stiffness, are the ones who undergo this procedure the most frequently. In this procedure, implants that replicate the joint's natural movement are used to replace the damaged surfaces of the thigh bone (femur), shin bone (tibia), and underside of the kneecap (patella).
Replacement of Parts of the Knee
Compared to a total knee replacement, a partial one is less invasive. It is used when only one knee joint component is injured, typically the patellofemoral (front), medial (inner), or lateral (outer). Only the damaged area of the knee is replaced with artificial components during this procedure. Recovery is quicker than with a total knee replacement because there is less tissue damage and a smaller incision. Under supervised rehabilitation, patients can usually return to activities like walking, climbing stairs, and even cycling in a few weeks.
Patellofemoral Arthroplasty, or Kneecap Replacement
When damage is restricted to the underside of the kneecap and the groove it rests in, a specialised procedure known as kneecap replacement, or patellofemoral arthroplasty, is carried out. The patellofemoral compartment, a portion of the joint, may wear down as a result of injury or arthritis. Only the rear of the kneecap and its femur groove are implanted again during this procedure. For younger patients or those with isolated arthritis, this is the best option.
Revision Knee Replacement
When a knee replacement that has already been implanted fails, becomes loose, or wears out over time, revision surgery is required. This procedure involves removing worn-out or damaged parts and replacing them with new ones. It is often more complex than the initial surgery because it may involve bone grafts or special implants to deal with bone loss or instability. Recovery may also take longer. However, it provides a second chance at mobility and comfort for patients who are still struggling with pain or limited function after their first knee replacement.
Take the Right Step Toward Pain-Free Movement!
You don't have to accept knee pain as the new normal. Whether you have mild discomfort from everyday wear and tear or severe arthritis that limits your range of motion, prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can make all the difference. From simple home remedies and low-impact exercises to advanced surgical options like total or partial knee replacement, there’s a solution tailored to every condition and lifestyle.
So, reach out to Apollo Spectra today. We offer individualised treatment plans, cutting-edge diagnostics, and consultations with leading orthopaedic specialists, all under one roof.
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment

.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








