What uterine fibroids are and how a laparoscopic surgery helps
September 26, 2022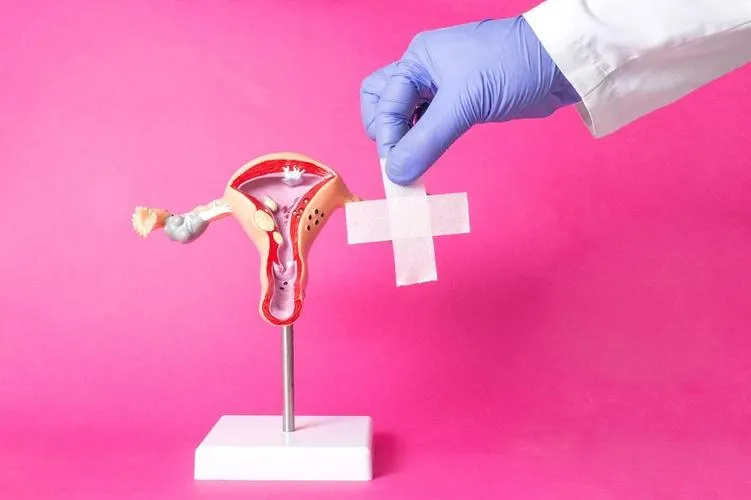
Uterine fibroids are benign tumours that grow in and on the uterus. Fibroids don't always create symptoms, but heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, frequent urination, and pain during sex are common when they do. Small fibroids usually do not require treatment, larger fibroids may require medication or surgery.
What are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids (also known as leiomyomas) are fibroids made of muscle and connective tissue. In most cases, these growths aren't malignant (benign). The uterus is a pear-shaped organ in the pelvis turned upside down. Your uterus is around the size of a lemon when it's normal. It's also known as the womb, where a kid develops and grows throughout pregnancy.
Fibroids can grow as a cluster or as a single nodule. Fibroid clusters can be as little as 1 mm in diameter or as large as 20 cm (8 inches). They can grow to be as big as, say, a watermelon. These tumours can develop inside the uterus's wall, inside the organ's main cavity, or even on the outside. Fibroids come in various sizes, numbers, and locations within and on the uterus.
With uterine fibroids, you may suffer a wide range of symptoms, which may or may not be the same as those experienced by another woman with fibroids. Because fibroids are so individual, your treatment will be tailored to your situation.
Are fibroids common?
Fibroids are a form of growth in your pelvis that are quite common. Fibroids affect anywhere from 40% to 80% of women. On the other hand, many women are unaware that they have fibroids since they have no symptoms. It can happen if you have little fibroids, which are asymptomatic because they don't show any symptoms.
Where do fibroids grow?
Fibroids can grow in various locations, both inside and outside the uterus. For your therapy, the location and size of your fibroids are critical. Your fibroids' location, size, and the number you have will influence which treatment option is best for you, if treatment is required.
Different names refer to the locations of your fibroids in and on the uterus. These names indicate the fibroid's location as well as its attachment. Uterine fibroids can occur in a variety of places, including the following:
- Fibroids that grow inside the uterine cavity (cavity) where a baby develops during pregnancy are called submucosal fibroids. Consider the growths that are stretching down into the uterus's empty region.
- Fibroids that are lodged in the uterine wall are known as intramural fibroids. Imagine the uterus's sides as walls in a house. Inside the muscle wall, fibroids can be proliferating.
- Subserosal fibroids: These fibroids are attached closely to the exterior wall of the uterus and are found on the outside of the uterus this time.
- Pedunculated fibroids: These fibroids are found on the exterior of the uterus and are the least prevalent form. Pedunculated fibroids have slender stems that connect them to the uterus. Because they have stalks and then considerably wider tops, they're mushroom-like.
How are uterine fibroids treated?
Treatment via laparoscopic fibroid removal
Uterine fibroids are benign (noncancerous) growths in a woman's uterus. Laparoscopic fibroid removal is a minimally invasive procedure. Uterine fibroid symptoms include excessively heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and bladder or bowel pressure.
Laparoscopic fibroid removal eliminates the need for traditional open surgery by inserting small, specialised surgical equipment through one or more small incisions in the belly. Patients benefit from shorter hospital stays, if any, less discomfort, and a quicker recovery and resumption to normal activities.
Laparoscopic fibroid removal options include:
Laparoscopic or robotic myomectomy — a minimally invasive treatment that removes fibroids while leaving the uterus intact, making it a desirable choice for women who want to get pregnant. Fibroids developing on the exterior of the uterus are frequently removed with this method. Robotic surgical technology can be employed in some circumstances, allowing women with complex illnesses to have a minimally invasive operation instead of an open surgery.
The uterus is removed by a minimally invasive operation called laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy. The most prevalent reason for a laparoscopic hysterectomy is the presence of fibroids. Women who desire to have children or retain their uterus should avoid this fibroid treatment. In some situations, robotic surgical equipment can perform a da Vinci hysterectomy, which allows women who would otherwise need an open surgery to have a less invasive operation instead.
Conclusion
Uterine fibroids are a frequent problem that many women face at some point in their lives. Fibroids might be tiny and cause no symptoms at all in rare circumstances. Fibroids can also create difficult symptoms at times. If you are experiencing any discomfort or pain, contact your healthcare professional. Fibroids can be treated, and your symptoms can often be alleviated.
Request an appointment at Apollo Spectra Hospitals, Call 1860500224
Fibroids are spherical growths that resemble smooth muscle tissue nodules. In some situations, they can be affixed to a slender stem.
A fibroid that develops into a cancerous or malignant tumour is extremely uncommon. Fibroids can cause cancer in one out of every 350 women. In detecting rare fibroid-related malignancies, no diagnosis is 100 percent accurate. Women with uterine fibroids that are rapidly growing or fibroids that are growing during menopause should be checked right away.
Uterine fibroids can happen to anyone. A variety of reasons can cause fibroids. Among them are: Obesity and higher body weight (a person is obese if their weight exceeds 20% of their ideal weight) Fibroids run in the family Not having children Menstruation starts early (getting your period at a young age) Menopause occurs at a late stage in life
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment

.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








